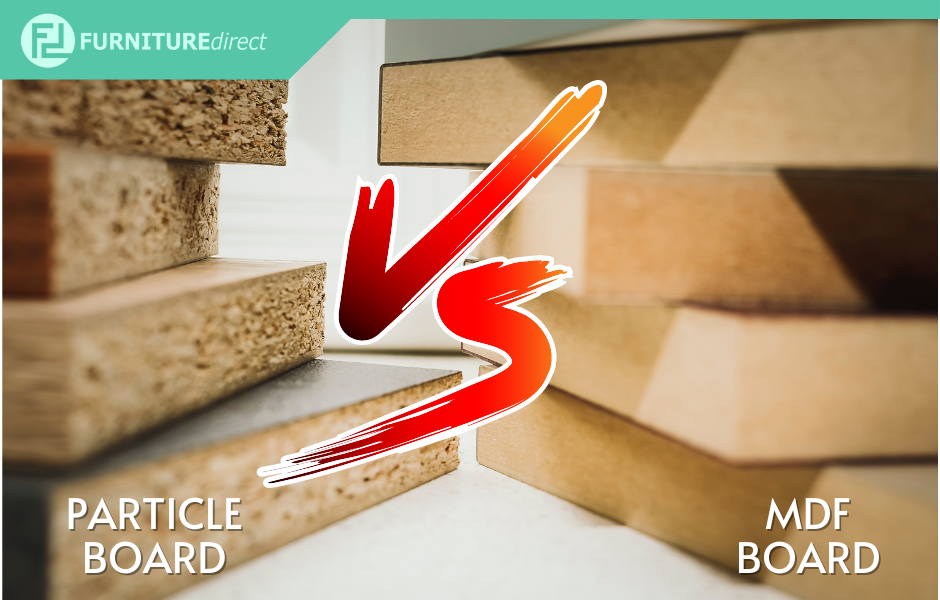
Particle board and MDF (medium-density fiberboard) are both engineered wood products that are made by compressing wood fibers and resin binders under high pressure and temperature. However, there are some differences between the two materials:
- Composition: Particle board is made from wood chips, shavings, and sawdust that are mixed with a resin binder and compressed. MDF, on the other hand, is made from wood fibers that are broken down and combined with resin binders to create a denser panel.
- Density: MDF is generally denser and heavier than particle board due to the finer wood fibers used in its composition. This makes MDF more durable and resistant to cracking or splitting, but it also makes it harder to work with compared to particle board.
- Surface quality: MDF has a smoother and more uniform surface than particle board, which makes it easier to paint or veneer. Particle board can have a rougher surface and may require more sanding or preparation before painting or finishing.
- Moisture resistance: MDF is more moisture-resistant than particle board, which can make it a better choice for high-humidity environments such as bathrooms or kitchens. Particle board can be more prone to swelling or warping if exposed to moisture.
Overall, MDF is generally considered to be a higher-quality material than particle board due to its increased density and smoother surface. However, both materials have their own advantages and disadvantages and can be suitable for different applications depending on the specific needs of the project.









































 Office Storage
Office Storage Steel Cabinet
Steel Cabinet

